Ecosystem and Habitat
Understanding the relationships and interactions of elements in the ecosystem and habitat where cheetahs live is crucial for any conservation and management efforts. Understanding of subjects in this area can help answer questions such as “what animals do cheetahs prey on and eat” and “what are its roles in its habitat and relationships with other species of animals”.
Where Cheetahs Live
Cheetah Habitat

African savannas have rich fauna biodiversity and house the habitats of a wide range of wildlife.
Animals, includes cheetah, are adapted to live in specific habitats. Cheetahs live mainly in grassland savanna. They prefer habitat which includes some cover in the form of bushes, medium length grass, trees, and small hills. Cheetahs need abundant prey in their habitat to survive and reproduce. In Namibia their habitat is densely bushed due to bush encroachment.
Cheetahs sometimes live in a wide variety of habitats. They occasionally use semi-desert, dense woodland or mountainous terrain. Older animals unable to defend territories and young cheetahs just starting to live on their own use these marginal habitats.


Namibian Biomes
Namibia is a country with rich biodiversity, as its land spans over five distinct types of biomes.
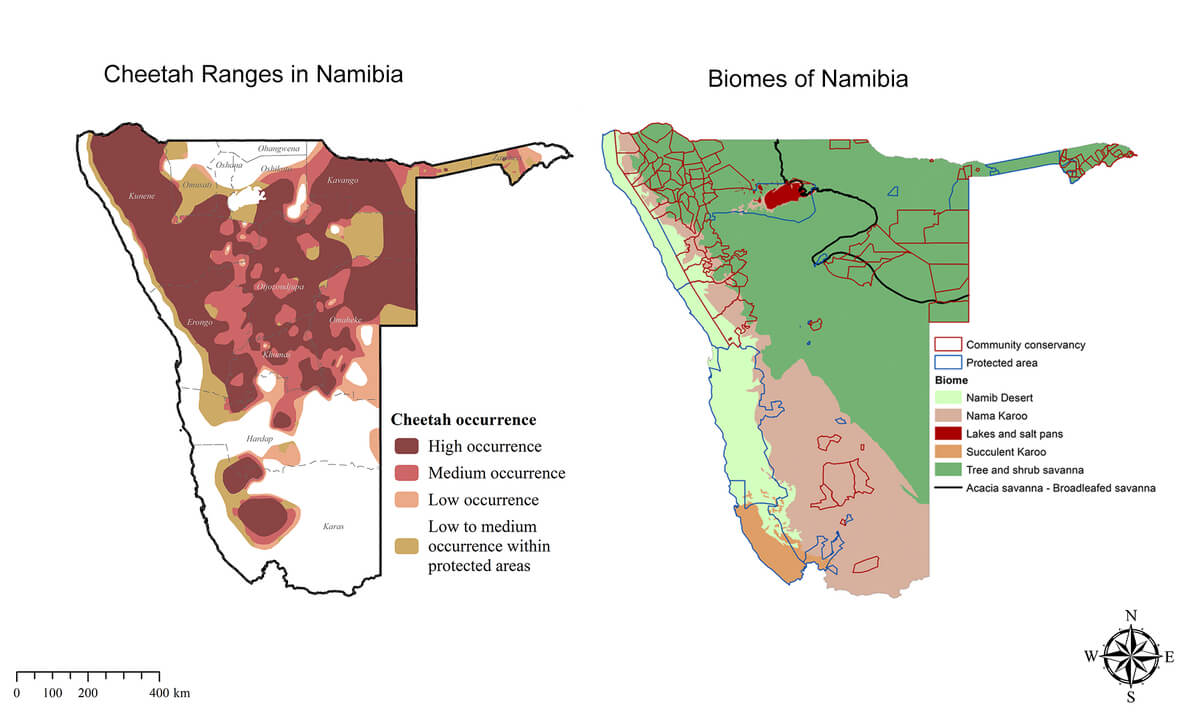
Map of Namibian biomes and cheetah ranges in Namibia. Cheetahs prefer the savanna biome which supports the animals they prey on.

The Cheetah’s Prey
Cheetahs prefer game to livestock
Cheetahs are born to prey on wild game, and will instinctually go after them. Cheetahs only go after livestock as a last resort when wild game is not available. This makes maintaining healthy ecosystems very important.
Cheetahs hunt mostly small antelope, young of large antelope, warthog, hare and game birds. They may take livestock in exceptional or opportunistic cases.
Cheetahs prefer game to livestock.
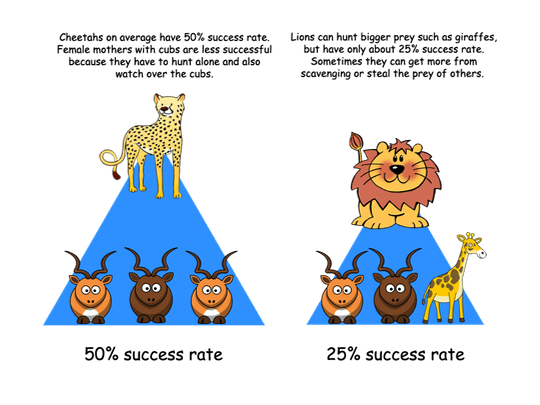
The cheetah’s lightweight build limits the size of prey they catch. Male coalitions can, however, overcome larger prey. Coalitions also stand a better chance at defending their prey against competitors than single cheetahs.
Predators have to work very hard to catch their prey. Cheetahs need to carefully select the animal they are most likely to catch. For this reason cheetahs, like all other predators, target animals that are old, sick, very young, injured, or slow. This allows only the strongest to survive and pass on their genes, thus maintaining a healthier game population.

Cheetahs in a coalition need to work together as a team to bring down larger and stronger prey, such as this wildebeest.

One of cheetahs' favorite type of prey are the gazelles, although they are very vigilant, fast and agile, thus are hard to catch.
Cheetah’s Role in the Ecosystem
Cheetah’s role
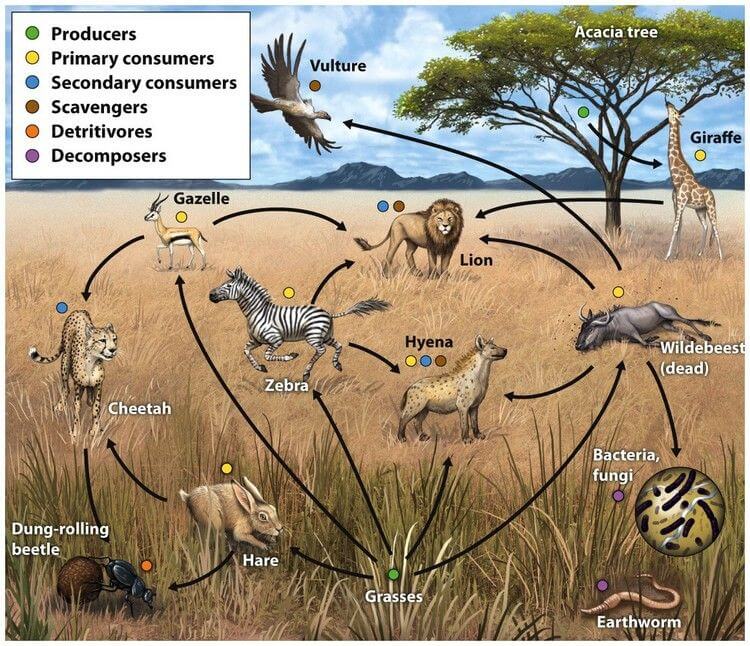
A simplified illustration of the food web of a savanna ecosystem.
Every animal species has its role (or niche) in the ecosystem that it lives in. As a carnivorous predator, the cheetah’s role in the ecosystem is important as it helps to maintain balanced and healthy food webs.
One of the cheetah’s roles in the ecosystem is to help keep the population of grazing animals at a healthy state. Because of the fact that cheetahs do not have the strength to go after big games such as adult wildebeest, elands, and kudus, they go after the ones that are young, weak, or sick. This helps to ensure that only the strongest of those species will survive, and also the populations of those species won’t reach the limit the ecosystem could handle such that it will have negative consequences.
Relationships with other species
Perhaps the cheetahs’ closest interactions with other species of animals other than the ones preyed upon are their competitors. While there are no species of animals that solely prey on the cheetahs as a food source, many compete with the cheetahs for food, territory, and dominance. Lions, leopards, and hyenas are the most formidable competitors that would come into the way of the cheetahs.
Despite the fact that competitions inevitably lead to casualties, it is an important aspect of any healthy ecosystem. Competitions ensure that no species of animal absolutely dominates all the resources in a territory, and resources are partitioned accordingly among the competing species as much as possible to minimize conflict. This leads to a balanced ecosystem with the most biodiversity, as each species is unique in its role within the ecosystem.

Hyenas often try to either steal cheetahs' killed preys or scavenge on the remains.

Lions will often take over the cheetah's prey easily as they are superior in strength.